Chinese Gold Financing Deals Explained
One of the main causes some of my colleague gold analysts assume SGE withdrawals are inflated and cannot be used as a measure for Chinese wholesale gold demand, is because of Chinese Commodity Financing Deals (CCFDs). However, this analysis is incorrect as will be demonstrated in this post.
Round Tripping And Chinese Gold Trade Rules
CCFDs are ways for Chinese speculators to acquire cheap funds using commodities as collateral. When it comes to using gold as collateral for CCFD there are two options: round tripping and gold leasing. What is round tripping? Goldman Sachs (GS) has properly explained the process in a report dated March 2014. From GS [brackets added by me]:
While commodity financing [round tripping] deals are very complicated, the general idea is that arbitrageurs borrow short-term FX loans from onshore banks in the form of LC (letter of credit) to import commodities and then re-export the warrants (a document issued by logistic companies which represent the ownership of the underlying asset) to bring in the low cost foreign capital (hot money) and then circulate the whole process several times per year. As a result, the total outstanding FX loans associated with these commodity financing deals is determined by:
- – the volume of physical inventories that is involved
- – commodity prices
- – the number of circulations
Our understanding is that the commodities that are involved in the financing deals include gold, copper, iron ore, and to a lesser extent, nickel, zinc, aluminum, soybean, palm oil and rubber.
…Chinese gold financing deals are processed in a different way compared with copper financing deals, though both are aimed at facilitating low cost foreign capital inflow to China. Specifically, gold financing deals involve the physical import of gold and export of gold semi-fabricated products to bring the FX into China; as a result, China’s trade data does reflect, at least partially, the scale of China gold financing deals. In contrast, Chinese copper financing deals do not need to physically move the physical copper in and out of China, so it is not shown in trade data published by China customs. In detail, Chinese gold financing deals includes four steps:
- Onshore gold manufacturers pay LCs to offshore subsidiaries and import gold from Hong Kong to mainland China – inflating import numbers
- offshore subsidiaries borrow USD from offshore banks via collaterizing LCs received
- onshore manufacturers get paid by USD from offshore subsidiaries and export the gold semi-fabricated products – inflating export numbers
- repeat step 1-3
Important to understand is that gold in round tripping needs to be physically imported into China and then exported, in contrast to copper. The reason being, which GS fails to mention, that the trade rules for gold in China are different than for all other commodities.
General Trade vs Processing Trade
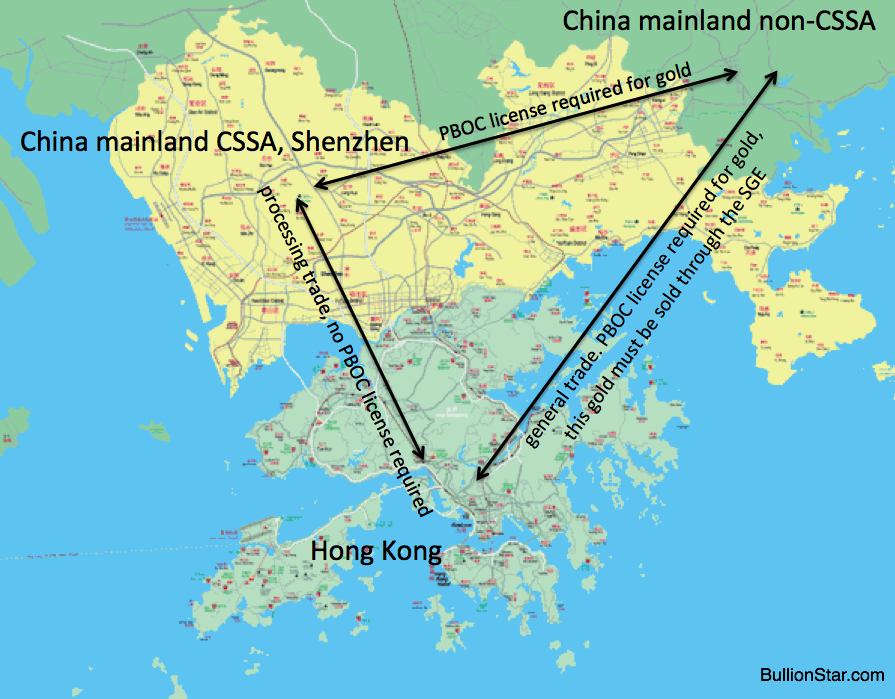
In essence gold bullion is prohibited from being exported out of the Chinese domestic gold market by the PBOC in general trade. For general trade fifteen banks enjoy a PBOC license to import gold.
- Shenzhen Development Bank / Ping An Bank
- Industrial and Commercial Bank of China
- Shanghai Pudong Development Bank
- Agricultural Bank of China
- China Construction Bank
- Bank of Communications
- China Merchants Bank
- China Minsheng Bank
- Standard Chartered
- Bank of Shanghai
- Industrial Bank
- Bank of China
- Everbright
- HSBC
- ANZ
All bullion imported through general trade is required to be sold first through the SGE, and consequently all gold flowing through the SGE is prohibited from being exported. Detail: a few jewelry companies also have a gold trade license for general trade, but this is insignificant. But there is more to it, which is another form of cross-border trade; processing trade. To explain what processing trade is, it would be best to first describe why it exists.
Since 2002 the State Council is active in stimulating the Chinese population to accumulate physical gold. Through commercial banks the Chinese people are informed about gold’s function in the economy and able to purchase gold granted of the finest quality. They can submit for a gold savings account, speculate in paper gold on the SGE or buy physical gold directly at the SGE, all through a commercial bank as a broker.
Some examples of how state-owned banks promote gold, from the Agricultural Bank China:
Physical gold is both a commodity and a financial product. It can be a gift or collection and may serve as an important investment vehicle for realizing preservation and appreciation. With a distinctive preservation function, physical gold is powerful to defend against inflation.
From ICBC:
☆ Considerations
1. Do not stop when gold price is low. Gold price may go up or down depending on the political and economic conditions and many other factors. Only by constant accumulation will the overall investment cost be reduced.
2. Persistence is the key. Investment risk is reduced by the average cost, the longer the investment period, the better in mitigating the impact of the fluctuation in gold price. When the market rallies, the gain will be protected and increase the investment.


The State Council’s strategy is to import as much gold as possible and export nil in order to build a strong economic and financial security barrier for China.
However, China doesn’t want to be left out in the global jewelry fabrication market, for which gold is required to be exported. To make China participate in the global jewelry fabrication market Chinese jewelry companies can import and export gold through processing trade. This is how it works, simplified:
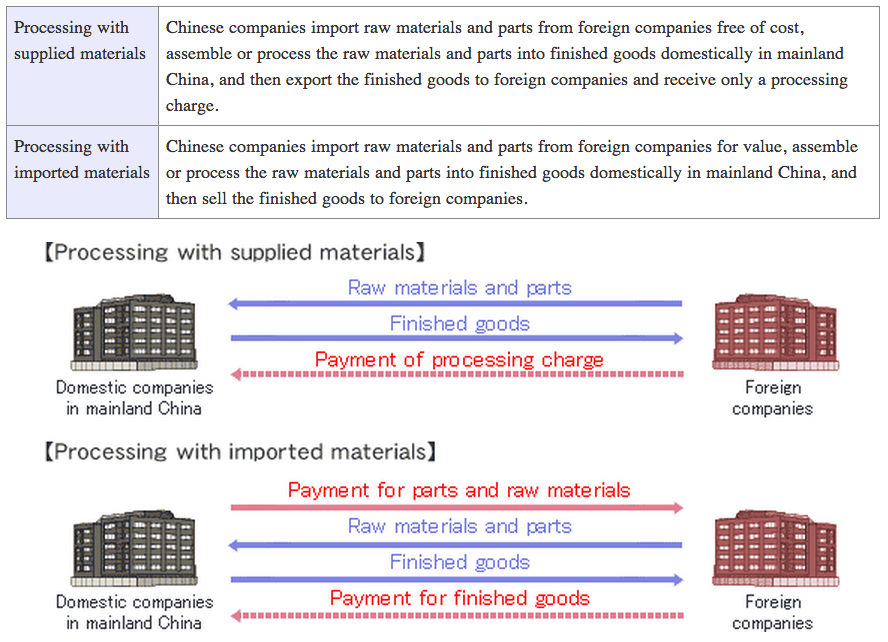
In processing trade raw materials from abroad are imported, processed into finished goods and then these products are required to be exported. This processing is usually done (there can be exceptions) in Customs Specially Supervised Areas (CSSA), also called Free Trade Zones (FTZ). Gold processing trade doesn’t require a general gold trade license from the PBOC. Note, to export gold from a CSSA to a non-CSSA (the rest of the mainland) a general gold trade license from the PBOC is required.
The next illustration demonstrates two types of processing trade.
An example for a processing trade would be; gold from Hong Kong is exported to Shenzhen (a CSSA just across the border from Hong Kong and well known for its vast jewelry industry; 4000 manufacturers), then the gold is fabricated into “jewelry” (/changed in shape or form/processed) and imported back into Hong Kong. By the way, this trade would show up in Hong Kong’s customs report, but it wouldn’t affect Hong Kong net export to the mainland.
Through processing trade gold can be imported into/ exported out of China mainland, but these flows are completely separated from the Chinese domestic gold market where the SGE system operates. Gold imported through processing trade is therefor not required to be sold through the SGE – it is not even allowed to be traded through the SGE.
In the next illustration we can see Hong Kong (representing the rest of the world), the CSSA in Shenzhen and the mainland (the Chinese domestic god market).
Processing trade is often done between Hong Kong and Shenzhen; all gold exported from China (CSSA) to Hong Kong or any other foreign nation is processing trade.
Round tipping by Chinese speculators can only be done through processing trade; it simply isn’t possible through general trade, as in general trade gold is prohibited from being exported. Round tripping flows are completely separated from the Chinese domestic gold market and the SGE, hence, round tripping doesn’t inflate SGE withdrawals. Only by bending the rules, set up a fake gold jewelry company in a CSSA, speculators can import and export gold to round trip. Consequently, GS notes gold needs to be physically imported and exported for round tripping, in contrast to copper.
In theory the gold tied up in round tripping can be at max the amount of gold yearly exported from China (to Hong Kong), at minimum a far smaller amount that is being used in many cycles, in every cycle being counted as import and export. Round tripping doesn’t inflate net export from Hong Kong to China.
The Chinese Gold Lease Market
The other gold financing deal that can be used by Chinese speculators is gold leasing (which is exactly the same as a gold loan). In general gold leasing is a normal market practice. For the sake of simplicity, I have categorised all potential gold lessees (borrowers) in three groups (gold miners, jewelers and speculators) to have a look at some examples (with US dollars) to learn how gold leasing is done in financial markets:
- A gold miner needs funds to invest in new production goods. It can borrow dollars from a bank at an 7 % interest rate, or borrow gold from a central bank at 2 % – the gold lease rate is usually lower than the dollar interest rate. The miner chooses to borrow 10,000 ounces from a central bank and sells it spot at $1,500 an ounce. The proceeds are $15,000,000 that can be used to invest in new production goods. In a years time the miner has mined 10,200 ounces to repay the principal debt plus interest (the interest on gold loans can be settled in gold or dollars, depending on the contract). Through gold leasing the miner has acquired cheap funding, if compared to a dollar loan. The movement in the price of gold during the lease period is neglected in this example.
- A jeweler needs funds to buy gold stock for production. It can borrow dollars from a bank for 7 %, or borrow gold for 2 %. The jeweler borrows 10,000 ounces, with which it can start fabricating jewelry. To hedge itself against price fluctuations the jeweler can sell spot, for example, 10 % of the 10,000 ounces it has borrowed (1,000 ounces at $1,500 makes $1,500,000) to buy gold futures contracts in order to lock in a future price. After a year the jeweler has sold the 9,000 ounces (as jewelry) for dollars and can take delivery of the long futures contracts to repay the gold loan. If one buys (long) 10,000 ounces through a futures contract for delivery in a year’s time, initially he is required to pay a margin, for example 10 %. When the contract expires and he wants to take physical delivery he must pay the remaining 90 %.
- A pseculator is looking for cheap funds. It can borrow dollars from a bank for 7 %, or borrow gold for 2 %. He borrows 10,000 ounces, sells it spot at $1,500 an ounce. The proceeds are $15,000,000 and subsequently these newly acquired funds can be used to invest in higher yielding products (> 2 %). If the trader chooses to hedge itself in the futures market is up to him. After a year the 10,000 ounces plus interest need to be repaid, either the trader can purchase gold with the profits made on the higher yielding investment or from delivery of futures contracts.
In China all gold leases are settled through the SGE; both lessor (lender) and lessee are required to have an SGE Account. If a lease is agreed between two parties gold is transferred from one SGE Bullion Account to the other, when the lease comes due the gold is returned. At SGE level it’s as simple as that.
There is a big difference between jewelers that lease gold in contrast to miners and speculators. Jewelers lease gold because they need physical gold for fabrication; miners and speculators lease gold because they are seeking cheap funds, they will always sell the leased gold (without withdrawing the metal) spot at the SGE to use the proceeds. Why would a speculator withdrawal the metal?
Therefor, IF SGE withdrawals contain leased gold this is for jewelry fabrication that eventually ends up at retail level. When a jeweler needs to repay the lease it simply buys gold at the SGE, subsequently this gold will be transferred from his SGE Bullion Account to the lessor’s SGE Bullion Account. It’s not likely a jeweler would buy gold off-SGE to repay a lease, which than would need to be refined into newly cast bars by an SGE approved refiner to enter the SGE vaults and to be credited to the lessors SGE Bullion Account.
Phillip Klapwijk, analyst with Precious Metals Insights (PMI) in Hong Kong, previous Executive Chairman of Thomson Reuters GFMS and consultant for the World Gold Council, has stated there is 1,000 tonnes of gold tied up in CCFD (not true!). Additionally, he said:
… a good part of the withdrawals represent gold that is used purely for financing and other end-uses that are not equivalent to real consumption.
Needless to say I don’t agree. Am I the only one? No. When Na Liu of CNC Asset Management Ltd., visited the SGE in May 2014 he was told by the President of the SGE Transaction Department:
First, the withdrawal data reflects the actual gold wholesales in China. In 2013, the total gold withdrawal from the SGE vaults amounted to 2,196.96 tonnes. The President of SGE Transaction Department (The President) said: “This 2,200 tonnes of gold, after leaving our vaults, they entered thousands of Chinese households in the form of jewellery and investment purchases.”
… Second, none of the 2,200 tonnes of gold was bought by the Chinese central bank. The President said: “The PBOC does not buy gold through the SGE.”
… Third, the financing deals do not exaggerate SGE’s assessment of China’s gold demand. This is because “the financing deals do not take place after the gold leaves the vaults.”
The President of the SGE’s Transaction Department is clearly stating most leasing happens within the SGE system and the metal is not withdrawn. I’m not saying it can’t occur a speculator would withdrawal metal from the SGE vaults, but in general he would not. Therefor, gold leasing by speculators does not inflate SGE withdrawals and therefor does not explain the difference between SGE withdrawals and Chinese consumer gold demand as disclosed by the World Gold Council.
As mentioned before jewelers do withdraw gold from the SGE vaults, but this is eventually to be sold as jewelry. However, the amount of gold leased and withdrawn by jewelers that has not yet been sold as jewelry, is stock inventory (likely hedged in the futures market) and thus can be excluded from gold demand depending on what metric is used.
The WGC had also stated in a report 1,000 tonnes was tied up in CCFD, based on PMI’s data. But, when I send the WGC an email to ask about the details, they replied [brackets adde by me]:
Gold leasing: Banks have built up this business to support China’s burgeoning gold industry. Miners, refiners and fabricators all have a requirement to borrow gold from time to time. For example, fabricators borrow gold to transform into jewelry, sell and then repay the bank with the proceeds. It is an effective way for the fabricator to use the bank’s balance sheet to fund its business. Banks have strict policies in place for who they can lend to, and these have been tightened over recent years, but during PMIs field research it identified that, in some instances, organizations other than genuine gold business had used this method to obtain gold, which it would then sell to obtain funding [in this case the gold wouldn’t be withdrawn from the SGE vaults]. It would then hedge its position. According to PMI, this can generate a lower cost of funding than borrowing directly from the bank. Our colleagues in China think this would be a very small part of total gold leasing; the majority of it would be used to meet the demands of genuine gold businesses.
Here the World Gold Council admits gold leases that are withdrawn from the SGE vaults are used for genuine gold business (being part of true gold demand). More confirmation gold leasing does not explain the difference.
More detailed information about the Chinese gold lease market can be found in my posts A Close Look At The Chinese Gold Lease Market, Gold Chat About The Chinese Gold Lease Market, Zooming In On The Chinese Gold Lease Market, Chinese Gold Leasing Not What It Seems and Reuters Spreads False Information Regarding The Chinese Gold Lease Market.
Conclusion
Round Tripping gold flows are completely separated from the Chinese domestic gold market (SGE) and gold leasing only inflates SGE withdrawals when used for genuine gold business. Therefor, SGE withdrawals equal Chinese wholesale gold demand.
Popular Blog Posts by Koos Jansen
 China’s Secret Gold Supplier is Singapore
China’s Secret Gold Supplier is Singapore
 Audits of U.S. Monetary Gold Severely Lack Credibility
Audits of U.S. Monetary Gold Severely Lack Credibility
 China Gold Import Jan-Sep 797t. Who’s Supplying?
China Gold Import Jan-Sep 797t. Who’s Supplying?
 The Gold-Backed-Oil-Yuan Futures Contract Myth
The Gold-Backed-Oil-Yuan Futures Contract Myth
 Estimated Chinese Gold Reserves Surpass 20,000t
Estimated Chinese Gold Reserves Surpass 20,000t
 Did the Dutch Central Bank Lie About Its Gold Bar List?
Did the Dutch Central Bank Lie About Its Gold Bar List?
 PBOC Gold Purchases: Separating Facts from Speculation
PBOC Gold Purchases: Separating Facts from Speculation
 U.S. Mint Releases New Fort Knox Audit Documentation
U.S. Mint Releases New Fort Knox Audit Documentation
 China Net Imported 1,300t of Gold in 2016
China Net Imported 1,300t of Gold in 2016
 Why SGE Withdrawals Equal Chinese Gold Demand and Why Not
Why SGE Withdrawals Equal Chinese Gold Demand and Why Not






 Koos Jansen
Koos Jansen